By Dr. Hans | January 2024
Article Outline:
- Introduction
- US Indications
- Understanding ED
- Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
- Penile Arteries and Veins
- Penile Duplex Ultrasound Protocol
- Penile US Benefits
Introduction
The significance of penile ultrasonography for medical professionals in the diagnosis and treatment of erectile dysfunction is paramount. Penile Doppler Ultrasound is a diagnostic technology that allows doctors to accurately assess blood flow within the cavernosal arteries and detect any abnormalities or blockages that contribute or cause erectile dysfunction.
“Doppler ultrasound is a gold standard for diagnosing injuries of the scrotum and penis.” (Al-Vadzhikh MA, 2023)
By providing real-time imaging of penile vasculature during both flaccidity and erection, this gold-standard technique enables healthcare providers to determine the underlying causes of impotence, whether they stem from venous leakage or arterial insufficiency. Moreover, by assessing peak systolic velocity and resistive index values obtained through penile doppler ultrasound examination, clinicians can further refine their diagnoses and tailor treatments accordingly. The recommended procedure for conducting a penile doppler ultrasound involves applying a gel on the penis followed by using a transducer device to emit high-frequency sound waves that penetrate deep into tissues while generating detailed images on a screen. This non-invasive technique is not only safe but also highly informative when it comes to guiding therapeutic interventions.
Ultimately, incorporating penile doppler ultrasound into clinical practice empowers medical professionals in effectively diagnosing and treating erectile dysfunction patients with precision and confidence while mitigating the inherent risks of misdiagnosis and poor treatment outcomes.
Keywords: Duplex color doppler ultrasonography, end diastolic velocity, erectile dysfunction, erection hardness score, International index of erectile function questionnaire, peak systolic velocity, phentolamine, prostaglandin – E1, time to erection
Introduction to Penile Doppler Ultrasound
Penile Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to evaluate the blood flow in the penis. It is a safe and painless procedure that can help diagnose the underlying causes of erectile dysfunction (ED). This diagnostic tool has revolutionized the evaluation of ED, providing valuable information about the structural and functional integrity of the penile arteries and veins.
LEARN MORE ABOUT PENILE DOPPLER ULTRASOUND
FIND A PENILE ULTRASOUND NEAR YOU
How Does Penile Doppler Ultrasound Work?
During a penile Doppler ultrasound, a small handheld device called a transducer is used to send and receive sound waves through the tissues of the penis. These sound waves bounce off blood cells, creating images that show how blood flows through the vessels. The transducer also measures the direction and speed of blood flow in real-time, allowing for accurate assessment of any abnormalities.
Indications for Penile Doppler Ultrasound
Penile Doppler ultrasound is primarily used to diagnose vasculogenic ED – that which results from inadequate blood flow to the penis. It may also be recommended when other potential causes have been ruled out or if there are concerns about damage or blockage in the penile arteries or veins.
Some common indications for penile doppler ultrasound include:
– Erectile Dysfunction: Especially if other treatment options have failed.
– Peyronie’s Disease: PD is a condition where scar tissue forms inside the penis, causing curvature during erections.
Explanation of what ultrasonography is and its use in medical imaging
Ultrasonography, also known as ultrasound imaging or sonography, is a non-invasive medical technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of internal body structures. It is mainly used for diagnostic purposes and has become an essential tool in modern medicine, particularly in the field of radiology.
In ultrasonography, a handheld device called a transducer emits high-frequency sound waves into the body. These waves travel through the different tissues in the body and are reflected back to the transducer at varying speeds depending on the density of the tissue they encounter.
The transducer then converts these sound waves into electrical signals, which are then processed by a computer to create images or videos of the internal organs and structures.
One major advantage of ultrasonography is its safety profile. Unlike other medical imaging techniques such as X-rays or computed tomography (CT), ultrasound does not use ionizing radiation, making it safe for repeated use without potential harm to patients. It is also non-invasive and painless, making it suitable for all age groups and even pregnant women.
Ultrasound imaging has various applications in medical diagnosis and treatment planning. It is commonly used to evaluate soft tissues such as muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints. It can also provide detailed images of internal organs like the heart, liver, kidneys, bladder, and reproductive organs.
In recent years, ultrasonography has gained significant recognition for its role in diagnosing erectile dysfunction (ED). ED is a condition where a man
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is crucial in addressing and treating the condition effectively. ED, also known as impotence, is defined as the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. ED affects approximately 30 million men in the United States alone and its prevalence increases with age. (Sooriyamoorthy, 2023)
The causes of ED can be physical, psychological, or a combination of both. Physical causes include diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, and hormonal imbalances. Lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity can also contribute to ED. Psychological factors that may lead to ED include stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship issues.
The penis contains arteries that pump blood to the penis, causing an erection. The arterial supply to the penis is the internal pudendal arteries, which become the penile arteries. Each penile artery terminates in bulbar, urethral, dorsal, and cavernosal arteries. The paired cavernosal arteries penetrate the tunica albuginea and enter the crura of the corpora cavernosa. Reduced arterial blood flow to or through the aforementioned arteries results in vasculogenic Erectile Dysfunction.
Sustained hypoxia caused by decreased delivery of oxygen to the penis results in cellular death that presents clinically as:
- Atherosclerosis
- Venous insufficiency
- Fibrous scar tissue
- Peripheral nerve death
Because the penis is peripheral in anatomical relation to the body, decreased delivery of oxygen to the penile tissues results in impaired removal of metabolites from the penile tissues and may develop into Neurogenic Erectile Dysfunction- similar to peripheral neuropathy.
To understand the root causes of ED, a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is necessary. This may involve taking a detailed medical history and performing various physical examinations and laboratory tests.
One important tool that has been increasingly used in diagnosing ED is Penile Doppler Ultrasound (PDU). PDU uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of blood flow within the penis. This allows for the assessment of penile blood flow during different stages of arousal.
In cases where there are physical causes of ED such as arterial insufficiency or venous leakage (blood leaking out from the penis), PDU can provide valuable information about these conditions. It can also help identify any structural abnormalities in the arteries or veins supplying blood to the penis.
Clinical Review Of Erectile Dysfunction
Definition of Erectile Dysfunction (ED):
Erectile dysfunction, also known as impotence, is a medical condition in which a man has difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. It can have a significant impact on a man’s self-esteem and overall quality of life.
Common Causes of ED:
There are various physical and psychological factors that can contribute to the development of erectile dysfunction. Some common causes include:
1. Physical Causes:
– Cardiovascular diseases: Conditions like high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, and diabetes can damage the blood vessels and nerves that supply blood to the penis, leading to ED.
– Hormonal imbalances: Low levels of testosterone or thyroid hormones can affect sexual function.
– Neurological disorders: Conditions such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and spinal cord injuries can interfere with nerve signals that control erections.
– Structural issues: Anatomical abnormalities in the penis or pelvic area can cause ED.
– Medications: Certain medications used to treat high blood pressure, depression, or prostate conditions may have side effects that contribute to erectile dysfunction.
2. Psychological Causes:
– Performance anxiety: Stress related to sexual performance can lead to temporary episodes of ED.
– Depression and other mental health issues: These conditions can affect libido and sexual desire.
– Relationship problems: Difficulties in relationships or communication with one’s partner can lead to feelings of inadequacy and contribute to ED.
It is essential to highlight that within the context of Erectile Dysfunction (ED), the causes are not mutually exclusive but rather frequently coexist as comorbidities. Comorbidity refers to the simultaneous presence of two or more medical conditions in an individual. In the case of ED, it is imperative to understand that various factors can contribute to its development, and these factors often intertwine and exacerbate one another.
The Importance of Accurate ED Diagnosis
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition that affects millions of men worldwide. It can have a significant impact on a man’s self-esteem, relationships, and overall quality of life. While there are various treatment options available for ED, the first step towards successful management is an accurate diagnosis.
Accurate diagnosis of ED is crucial as it helps identify the underlying cause of the condition. This allows for targeted treatment and better outcomes. In many cases, ED may be a symptom of an underlying medical condition that requires prompt attention.
One of the essential tools in diagnosing ED is penile Doppler ultrasound, also known as penile duplex or color flow imaging. This non-invasive procedure uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of blood flow within the penis. It allows for a detailed evaluation of the anatomy and function of the arteries and veins in the penis.
Accurate diagnosis through penile Doppler ultrasound can help identify several potential causes of ED:
1. Vascular problems: The most common cause of ED is reduced blood flow to the penis due to narrowing or blockage in the blood vessels (arteries). Penile Doppler ultrasound can detect any abnormalities in these blood vessels and help determine if there are any obstructions that may be causing erectile difficulties.
2. Neurological issues: Nerves play a critical role in initiating and maintaining an erection by sending signals from the brain to the penis. Any damage or impairment to these nerves can result in ED.
How Penile Doppler Ultrasound Works
Penile Doppler Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to examine the blood flow in the arteries and veins of the penis. It is an important tool in diagnosing the root causes of erectile dysfunction (ED) as it provides detailed information about the blood supply to the penile region.
The procedure involves using a handheld device called a transducer, which emits high-frequency sound waves that bounce off tissues and create echoes. These echoes are then converted into images by a computer, allowing doctors to see real-time images of the blood vessels in the penis.
General US Procedure Overview
During a Penile Doppler Ultrasound, the patient will be asked to lie on their back with their genitals exposed. The doctor will apply a gel to help transmit sound waves and ensure good contact between the transducer and skin. The transducer is then moved over different areas of the penis, including both sides of the shaft, base, and tip.
The ultrasound technician can additionally take measurements of blood flow velocity using color Doppler imaging. This allows them to assess whether there are any obstructions or abnormalities in blood flow within the penile arteries. This test requires the intracavernosal injection of a vasoactive medication, such as Alprostadil, to elicit a partial erection.
One common cause of ED is a condition known as arteriogenic ED, where there is inadequate arterial inflow of blood prerequisite to achieve an adequate localized blood pressure needed to maintain an erection. Penile Doppler Ultrasound can accurately detect this condition by measuring how quickly blood flows through certain areas of the penis.
If there is poor arterial inflow observed during Penile Doppler Ultrasound, further tests may be recommended, such as;
- Cavernosography
- CT Scan
- MRI Imaging
The choice of imaging modality for the penis depends on the specific clinical indication, suspected pathology, and availability of equipment.
Examining Arterial and Venous Blood Flow with a Linear Doppler Ultrasound Device
Penile Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses sound waves to produce images of the blood vessels and tissues within the penis. It has become an important tool in diagnosing erectile dysfunction (ED) as it provides valuable information about the blood flow in and around the penile region.
Linear Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique used to assess blood flow in arteries and veins. It utilizes sound waves to visualize the direction and speed of blood movement within the vessels.
In this section, we will provide a step-by-step breakdown of the procedure involved in performing penile Doppler ultrasound and discuss its purpose in diagnosing ED.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on using a linear Doppler ultrasound device for evaluating penile blood flow:
Penile Duplex Ultrasound Protocol
Exam Preparation:
- Prepare Equipment: Ensure you have the necessary equipment, including:
- Linear Doppler ultrasound device with appropriate probes (e.g., 7-10 MHz for peripheral vessels)
- Ultrasound gel
- Tissue wipes
- Gloves
- Measurement calipers (optional)
- P.D.A.D. Peyronie’s Disease Assessment Device (optimal)
- Patient Positioning: Position the patient comfortably on an examination bed. Depending on the vessel being examined, different positions may be required. For example, examining the carotid arteries might involve having the patient lie at a 45-degree angle with their head turned slightly away from the side being assessed.
- Probe Selection: Choose the appropriate probe based on the depth and size of the target vessel. Higher frequencies provide better resolution for superficial vessels, while lower frequencies penetrate deeper tissues.
- Recommended linear probe settings are between 7.5MHz to 10MHz
Penile Exam:
- Apply Gel: Apply a generous amount of ultrasound gel to the probe to improve acoustic coupling and image quality.
- Locate the Vessel: Gently place the probe on the skin overlying the target vessel. Use anatomical landmarks and palpation to guide probe placement.
- Optimize Image: Adjust the ultrasound settings, such as gain,depth, and focus, to obtain a clear visualization of the vessel lumen and surrounding tissues.
- B-mode Imaging: First, use B-mode (standard ultrasound) to visualize the vessel’s structure, size, and any surrounding abnormalities.
- Pulse Doppler Mode: Switch to pulse Doppler mode to assess blood flow.The Doppler signal will appear as a waveform on the screen,representing the velocity and direction of blood movement.
- Spectral Analysis: Analyze the Doppler waveform characteristics,including peak systolic velocity (PSV),end-diastolic velocity (EDV), and resistive index (RI), to evaluate blood flow patterns and identify potential abnormalities.
Specific Considerations for Arterial and Venous Flow:
- Arterial Flow: Focus on the PSV and RI. Typically, a high PSV and low RI indicate good arterial flow, while a low PSV and high RI suggest stenosis or blockage.
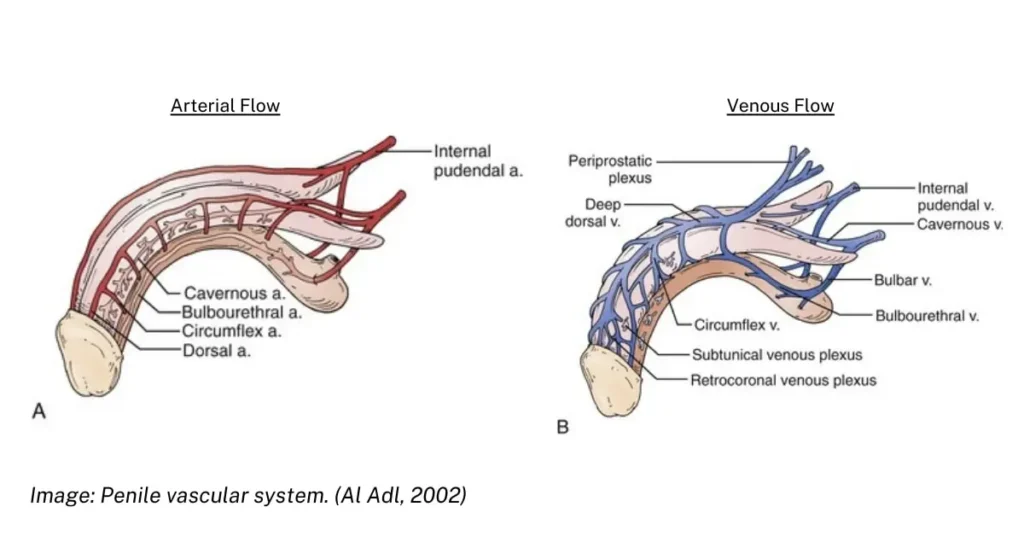
- Venous Flow: Assess the flow velocity throughout the cardiac cycle and look for signs of reflux (backward flow). Increased venous flow velocity and presence of reflux might indicate venous insufficiency.
Documentation and Reporting:
- Capture still images and video clips of the B-mode and Doppler waveforms for documentation and comparison.
- Document the findings, including vessel size, flow velocities, and any observed abnormalities, in a clear and concise report.
This is a general guideline, and specific protocols may vary depending on the clinical indication and the manufacturer’s recommendations for the ultrasound device.
- Performing and interpreting Doppler ultrasound examinations requires proper training and expertise. This procedure should only be conducted by qualified healthcare professionals.
Benefits of Penile Doppler Ultrasound
There are numerous benefits of using ultrasonography, specifically penile Doppler ultrasound, in identifying the root causes of erectile dysfunction (ED). This non-invasive and painless imaging technique has revolutionized the diagnosis and treatment of ED by providing detailed information about the structure and function of the penis.
1. Accurate Diagnosis:
Ultrasonography offers a highly accurate way to diagnose ED compared to traditional methods. It enables doctors to visualize the blood flow within the penile arteries and veins, which is crucial in determining if there is any blockage or narrowing that could be causing ED. This eliminates any guesswork and provides a more precise diagnosis.
2. Non-Invasive Procedure:
Penile Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive procedure, meaning it does not require any incisions or injections. Instead, it uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of internal structures. This makes it a safer option for patients who are uncomfortable with invasive procedures.
3. Painless and Quick:
The procedure itself is relatively quick, taking only 15-20 minutes to complete. It is also painless as no needles or probes are inserted into the body. The patient only needs to lie down on their back while an ultrasound technician moves a small handheld device over different areas of the penis.
4. Cost-Effective:
Compared to other diagnostic procedures such as angiography or MRI, penile Doppler ultrasound is significantly more cost-effective. It can provide similar results without requiring additional equipment or costly hospital stays.
The Impact of Incorrect ED Diagnosis on Treatment Outcomes
When it comes to treating any medical condition, an accurate diagnosis is crucial. This is especially true for erectile dysfunction (ED), a common and often emotionally distressing issue for many men. There are various methods of diagnosing the root cause of ED, and one such tool that has gained popularity in recent years is penile Doppler ultrasound.
However, if the diagnosis obtained through this imaging technique is incorrect, it can have a significant impact on treatment options and patient well-being. In this section, we will discuss the potential consequences of an incorrect diagnosis in relation to ED.
1. Delayed or Ineffective Treatment: One of the primary concerns with an incorrect diagnosis of ED is that it can delay or even lead to ineffective treatment. This happens when the underlying cause of ED is not accurately identified, and treatment is prescribed based on a misdiagnosis. For example, if a patient’s ED symptoms are caused by arterial insufficiency but are incorrectly diagnosed as psychological in nature, treatments such as counseling or medications may not be effective in improving their condition.
2. Unnecessary Treatments: On the other hand, an incorrect diagnosis can also result in unnecessary treatments being prescribed to patients. This could include invasive procedures like penile implants or surgeries that carry risks and may not be needed if the correct cause of ED was identified from the beginning.
3. Mental Health Impact: The emotional toll that comes with dealing with erectile dysfunction can already be overwhelming for many individuals. An incorrect diagnosis can add to this burden and greatly reduce patient satisfaction, chargebacks, and negative reviews. When patients bravely seek help for their intimate health concerns, they place a significant amount of trust in healthcare professionals to provide accurate diagnoses and appropriate treatment options. This emotional fallout of a misdiagnosis often leads to diminished overall satisfaction with medical services received while amplifying negative sentiments towards the healthcare practitioners involved. Moreover, financial repercussions arise as well: dissatisfied patients may request chargebacks for ineffective treatments or resort to leaving unfavorable online reviews that tarnish both individual reputations and clinic ratings.
Thus, ensuring accurate diagnoses is paramount not only for effective treatment but also for preserving patient well-being and maintaining positive professional relationships within the medical community.
Conclusion:
Penile ultrasound is an invaluable tool for physicians when it comes to the diagnosis and treatment of erectile dysfunction, holding immense significance in this realm. This article focuses on the clinical application of linear duplex ultrasound, specifically highlighting its efficacy in diagnosing vascular issues that are often associated with erectile dysfunction. By utilizing this technique, medical professionals can thoroughly examine the penile blood vessels and assess their functionality, helping to identify potential underlying causes of erectile dysfunction such as arterial insufficiency or venous leakages.
The non-invasive nature of penile ultrasound makes it a preferred choice amongst patients and allows for accurate measurements of blood flow dynamics during different stages of erection. With precise imaging capabilities, physicians can pinpoint any abnormalities within the vasculature system that may be hindering normal erectile function.
By incorporating penile ultrasound into the diagnostic workup, clinicians have a comprehensive understanding of each patient’s specific vascular condition related to erectile dysfunction—enabling them to tailor effective treatment plans accordingly and ultimately enhance patients’ quality of life.
References:
Al Adl, Ahmed. (2002). EVALUATION OF POTENCY AFTER NERVE SPARING CYSTOPROSTATECTOMY.
Al-Vadzhikh MA, Vinogradov IV. Urologiia. 2023;(2):80-82.
Buss RR, Sun W, Oppenheim RW. Adaptive roles of programmed cell death during nervous system development. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2006;29:1-35. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.29.051605.112800
Green DR, Llambi F. Cell Death Signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7(12):a006080. Published 2015 Dec 1. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a006080
Spiegel, Rory & Teeter, William & Sullivan, Scott & Tupchong, Keegan & Mohammed, Nabeel & Sutherland, Mark & Leibner, Evan & Rola, Philippe & Galvagno, Samuel & Murthi, Sarah. (2020). The use of venous Doppler to predict adverse kidney events in a general ICU cohort. Critical Care. 24. 615. 10.1186/s13054-020-03330-6.
Sooriyamoorthy T, Leslie SW. Erectile Dysfunction. [Updated 2023 May 30]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562253/
